News & Views: Market Sizing Update 2024: Has OA Hit A Peak?

Overview
Each year, Delta Think’s Market Sizing analyzes the value of the open access (OA) scholarly journals market. This is the revenue generated by providers or the costs incurred by buyers of content.
We estimate the OA segment of the market to have grown to just over $2.2bn in 2023. This is only a marginal growth over the previous year. It is a small fraction of the long-term historical growth of the OA segment.
A reduction in the output of the large OA-only publishers has had a profound effect on the market. It has benefited established publishers, who are seeing a growth in OA, even while the overall market softens. We expect this pattern to continue in 2024.
Have we reached peak open access? Have the underlying drivers of OA changed? And are we now in an era of lower OA growth?
Headline findings
Our models suggest the following headlines for open access market sizing:
We estimate that the OA market grew to just over $2.2bn in 2023.
- 2023’s OA market grew by just under 1.7% from 2022. This less than one tenth of its historic growth.
- We estimate the total scholarly journals market to have increased by 1.2% in 2023, compared with its long-term low single-digit growth around 5%.
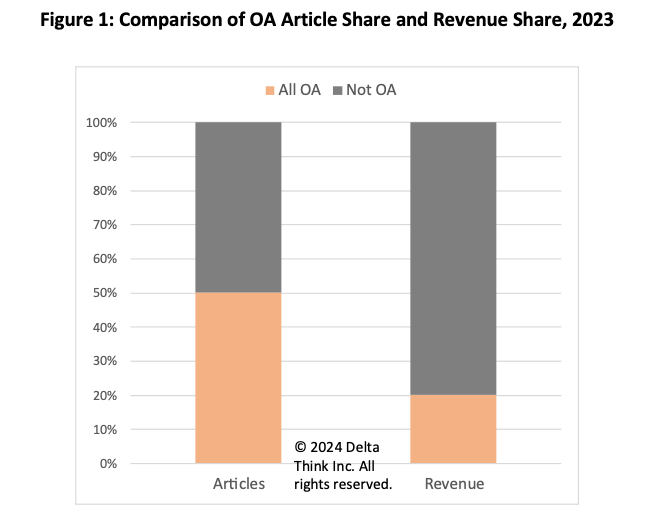
- Around 50% of all scholarly articles were published as paid-for open access in 2023, accounting for just over 20% of corresponding market value.
- The large fully open access publishers saw a significant drop in their output in 2023. We are likely also seeing the tail-end of the correction from the very high OA growth during COVID. This has led to a collapse in growth of fully OA output and revenue.
- Hybrid OA has taken up some of the shrinkage in fully OA. Growth in hybrid output and hybrid revenues continues to be strong.
- Without currency effects, growth would be even slower than the headline numbers suggest. Total OA value would have shrunk by 0.2%, and the overall journals market would have grown at 0.3%. This suggests that underlying growth in the OA market has stalled and that of the overall market grew at around one tenth of long-term trends.
- Growth in OA has shrunk to that of the underlying scholarly journals market.
- We anticipate a 2023-2026 CAGR (average growth each year) of 4.9% in OA output and 6.3% in OA market value. This is significantly lower than historical averages.
A note about our method
As ever, we are very grateful to the organizations that participate in our annual survey, which we anonymize and aggregate to inform our estimates. We will shortly send our usual detailed market update and analysis to participants, which breaks out fully OA and hybrid details.
Our market estimates focus on research publications for which money is likely to be paid, either to read or to publish. Our definition of open access excludes “bronze” (public access) and “green” (repository-only) articles.
Rather than simply looking at annual figures, we extract underlying trends to inform strategic decision-making. Each year our source data improves, and we can refine our view on resulting trends as more information becomes available. Therefore, each year we restate historic figures as needed to keep them up to date.
Trends
We have seen a stalling of OA growth in 2023, particularly in fully OA output. We are likely seeing a systemic shift to slower long-term growth as the underlying drivers of the market change.
The large OA-only publishers saw a significant drop in their output in 2023, and this has had a profound effect on the market.
- Clarivate’s delisting of journals from Web of Science had a knock-on effect across OA-only publishers’ portfolios and was likely the major driver of their decline in output, as authors chose other publication venues. OA publishers’ reduction in the use of special issues greatly reduces a major driver of their growth. Taken together, these two factors suggest we will see a much lower growth rate of fully OA output in future.
- Established publishers saw an increase in OA volume and value, even if the overall OA market has stalled. They have benefited from authors’ move away from the OA-only publishers. Hybrid OA has increased for the same reasons, and we anticipate that it will continue to grow strongly. Non-OA publishing is also seeing a slight uptick.
- Given the quality concerns around special issues, it seems unlikely that (many of) their articles would find other outlets, and so overall we are seeing growth in fully OA output stalling.
- We are likely also seeing the tail-end of the correction from the very high OA growth during COVID.
The data suggest that OA’s share of output has likely peaked in 2023.
- Our earlier sneak peek at the market suggested it peaked at 49% of output in 2022, falling to 48% in 2023. Our latest data here suggests OA just peaked at 50% share in 2022-2023 and may fall a few percentage points in the coming years.
- Results from our survey and anecdotal feedback suggest more of the same for 2024: large OA-only publishers are likely to see continued declines, while established publishers will see continued growth.
- The market will consolidate further. Long-term OA growth is likely to be less that it has been – perhaps mid-to-high single digits – but with increasing shares going to the larger publishers.
In 2023, around 50% of output was OA, accounting for around 20% of its value. This means that on average less money changes hands for OA articles than for non-OA ones.
- The gap between shares of value and volume has been closing historically but has remained roughly the same over the last couple of years.
- If the large OA-only publishers can recapture their early growth, then the gap will start narrowing again. However, it seems that established publishers are seeing a greater proportion of income from OA at the expense of others. This suggests the market-wide ratios will remain the same, but the specifics will vary depending on the publisher.
- Prices have increased, and we anticipate that this will continue, although the effects of mixed-model deals on pricing dynamics have yet to become clear. Hybrid revenues realized per article published remain higher than those published in fully OA journals, and we expect this trend to continue.
- OA is increasingly delivered as part of mixed-model deals, combining read and publish elements. If deals have price caps, it is possible that some of the OA output moving from OA publishers to larger publisher does not translate into higher OA revenues.
Conclusion
It’s difficult to make predictions – especially about the future. That said, we think that 2023 could prove to be a pivotal year for open access.
The challenges facing the big OA-only publishers in 2023 have been well-rehearsed. Delisting from Web of Science has led to an exodus of authors from across their portfolios. In 2022, we estimated that the big OA publishers – MDPI, Frontiers and Hindawi – together accounted for over 30% of OA market volume. It’s not surprising, then, that a decline in output from these publishers had a profound effect on the marketplace.
The results have been a mix of cannibalization and leakage. Established publishers and other access models have captured some of the publishing demand. Some content may have been subsumed into fixed-price deals, and so has not led to an increase in overall revenue. Then, given the quality concerns of special issues, it’s likely that a good proportion has simply disappeared. The signal to noise ratio has improved, and special issues are no longer fueling the growth that they once did.
The fundamental driver of OA used to be the policies of funder organizations. Now it appears to be those of Clarivate.
We have therefore seen a flatlining of OA growth, and OA share of output is struggling to get beyond 50%. Our models suggest it may pick up in the long term. But for now, at least, we estimate that its share has peaked.
Our industry does not systematically report comprehensive data about market volumes or value. So, any market sizing is an approximation, and figures should be taken as approximate. Subscribers to our Data & Analytics Tool can drill into the numbers in much greater depth, including analyzing fully OA vs. Hybrid OA details, society-specific output and subscription output. Please get in touch if you want to know more.
This article is © 2024 Delta Think, Inc. It is published under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. Please do get in touch if you want to use it in other contexts – we’re usually pretty accommodating.
TOP HEADLINES
Open Access Partnerships Key to Increasing the Global Impact of African Research – October 16, 2024
“The work of researchers in Africa is experiencing increased international reach, supported by new open access (OA) partnerships between research libraries and publishers. Recent forums in South Africa have highlighted the importance of this cooperation for the continued growth and impact of Africa’s rich research output.”
cOAlition S announces the release of an independent study on the impact of Plan S – October 15, 2024
“cOAlition S is pleased to announce the release of an independent, comprehensive study assessing the impact of Plan S on the scholarly communication landscape. Conducted by scidecode science consulting, following a tender process, this study provides the first assessment of the impact of Plan S five years after its launch.”
Over 50 Independent Publishers Commit to BioOne Subscribe to Open Pilot – October 8, 2024
“BioOne, the leading nonprofit aggregator in the biological, ecological, and environmental sciences, today announced that 71 titles from 54 global societies, museums, and research organizations will participate in its Subscribe to Open (S2O) pilot beginning in January 2026. This represents the largest number of independent publishers under a single S2O offer to date.”
Taylor & Francis Announces Subscribe to Open Journals Pilot – October 1, 2024
“Taylor & Francis has today announced its first Subscribe to Open (S2O) pilot, one of several innovative options it is trialing to accelerate open access (OA) publishing. S2O enables a journal’s subscribers to support its conversion to OA, making new articles available to readers everywhere.”
Update on UKRI’s journey to open access – September 16, 2024
“UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) is working collaboratively with stakeholders to support implementation of its open access policy. The policy applied since April 2022 for research articles and since January 2024 for monographs, book chapters and edited collections.”
OA JOURNAL LAUNCHES
October 17, 2024
EULAR Launches New Open-access Journal – EULAR Rheumatology Open (ERO)
“The European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR) proudly announces the launch of its new open-access journal, a pioneering platform dedicated to advancing research and knowledge in the field of rheumatology.”
October 7, 2024
Penn State University Libraries Open Publishing launches Stroke Clinician journal
“Penn State University Libraries’ Open Publishing program has partnered with the Association of Neurovascular Clinicians (ANVC) to launch a new open access clinical journal, Stroke Clinician.”
October 3, 2024
AIP Publishing to Launch New Open Access Journal, APL Computational Physics
“AIP Publishing announced today the latest addition in its open access portfolio, APL Computational Physics. The new journal is slated to open for submissions in early 2025.”
September 24, 2024
“The European Society of Endocrinology (ESE) is delighted to announce the launch of two new multidisciplinary, open-access journals, Environmental Endocrinology and Obesity and Endocrinology. The Journals will be published by Oxford University Press, with the launch issues scheduled for Q2 2025.”
September 17, 2024
IOP Publishing expands its open access environmental portfolio with Environmental Research: Water
“IOP Publishing (IOPP) is launching Environmental Research: Water a new open access (OA) journal which offers an interdisciplinary forum for researchers working to achieve water sustainability globally.”